-
Bahasa Indonesia
-
English
Oleh: Vincent Gaspersz, Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt & Certified Management System Lead Specialist
- APICS (www.apics.org) Certified in Production and Inventory Management (CPIM), Certified in Production and Inventory Management Fellow (CPIM-F), Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP), Certified Supply Chain Professional Fellow (CSCP-F);
- International Quality Federation (www.iqf.org) Six Sigma Master Black Belt (SSMBB);
- ASQ (www.asq.org) Certified Six Sigma Black Belt (CSSBB), Certified Quality Engineer (CQE), Certified Quality Auditor (CQA), Certified Manager of Quality/Organizational Excellence (CMQ/OE), Certified Quality Improvement Associate (CQIA);
- International Association for Six Sigma Certification (IASSC) Certified Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (ICBB);
- Registration Accreditation Board (www.exemplarglobal.org) Certified Management System Lead Specialist (CMSLS).
- Insinyur Profesional Utama (IPU) – Badan Kejuruan Teknik Industri- Persatuan Insinyur Indonesia (BKTI – PII)
- Asean Engineer Register (AER No. 10084), Asean Federation of Engineering Organizations (AFEO)
- Senior Member of the American Society for Quality (Member #: 00749775), International Member of the American Production and Inventory Control Society/Association for Supply Chain Management (Member #: 1023620), and Senior Member of the Institute of Industrial and Systems Engineers (Member #: 880194630).
Seperti telah disinggung oleh Vincent Gaspersz selama ini bahwa Sistem Pembelajaran di Indonesia adalah merupakan pembelajaran berpikir tingkat rendah (LOTS = Lower Order Thinking Skills), sehingga tidak bermanfaat dan tidak mampu mengakuisisi ilmu pengetahuan dan teknologi modern yang berlaku secara global. Untuk membahas dan menunjukkan pernyataan ini, maka akan ditunjukkan bagaimana pembelajaran ilmu statistika (statistics) yang sesungguhnya berguna untuk berkompetisi dalam pasar tenaga kerja global menjadi sia-sia belaka, karena lulusan perguruan tinggi, termasuk lulusan pendidikan statistika sekalipun tidak bisa berkontribusi secara signifikan dalam manajemen bisnis kelas dunia.
Pembelajaran statistika baru akan bermanfaat apabila kita mempelajari dan memahami minimum sampai pada tingkat menengah yaitu belajar tentang Statistical Engineering Methods yang bermanfaat bagi peningkatan kinerja sistem, atau lebih unggul jika kita memahami Statistical Thinking agar berkontribusi nyata dalam Systems Engineering and Systems Management.
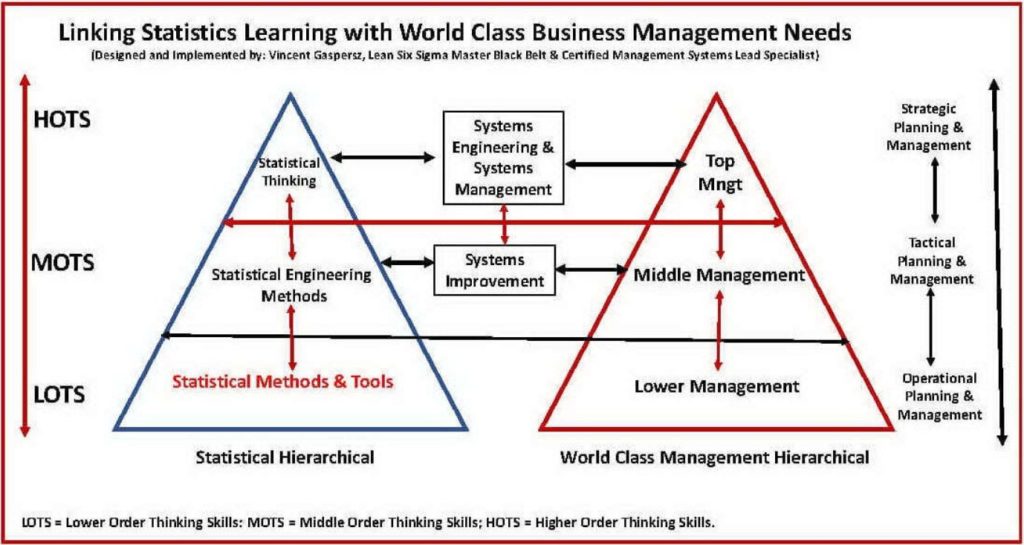
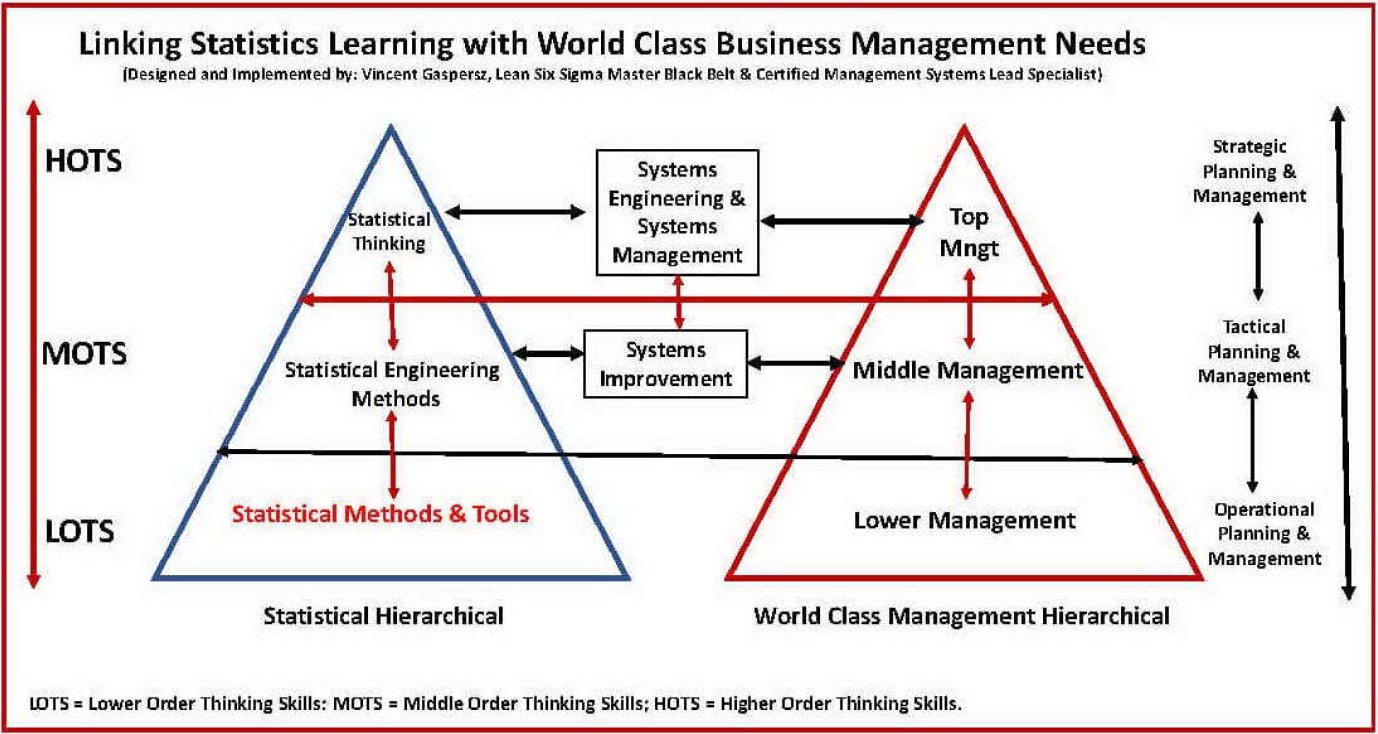
Pada dasarnya Statistika (Statistics) mempunyai tiga hirarki, yaitu: (1) Statistical Methods and Tools yang berada pada hirarki paling rendah, (2) Statistical Engineering Methods yang berada pada hirarki menengah, dan (3) Statistical Thinking yang berada pada hirarki paling tinggi.
Semua mahasiswa di Indonesia pasti telah mempelajari Statistical Methods and Tools ini, meskipun dengan pemahaman yang sangat kurang dan sering kali menerapkan secara salah karena kurangnya pemahaman terhadap asumsi-asumsi dan persyaratan dari aplikasi Statistical Methods and Tools itu.
Kesalahan-kesalahan Yang Sering Dilakukan
Kesalahan-kesalahan yang terlalu sering dibuat dan berulang terus-menerus dari dahulu sampai sekarang dalam menggunakan statistical tools tanpa memahami Statistical Engineering & Statistical Thinking!
Contoh kesalahan umum yang terlalu sering dilakukan oleh para mahasiswa dan/atau dosen termasuk ilmuwan dalam melaporkan hasil riset:
- Ho: X
- H1: Not X
Berdasarkan uji statistika bla bla bla, dengan taraf kepercayaan 99%, maka Ho DITERIMA! Ini adalah kesimpulan yang salah secara total, karena berarti kita belum memahami prinsip- prinsip Statistics! Tahukah kita bahwa Ho adalah hipotesis statistik yang dibuat BUKAN untuk DITERIMA? Seharusnya kesimpulan: berdasarkan taraf kepercayaan 99% menggunakan uji statistika xyz, maka belum CUKUP informasi untuk MENOLAK Ho. Hal ini TIDAK BERARTI kita MENERIMA Ho!
Setiap uji-uji statistika yang berkaitan dengan pengujian hipotesis, HANYA memberikan dua kesimpulan statistika berikut:
- Menolak Ho (dengan taraf kepercayaan sekian persen).
- Belum cukup informasi untuk Menolak Ho (dengan taraf kepercayaan tertentu); BUKAN (TIDAK BERARTI) Menerima Ho.
Silakan baca penjelasan lebih lanjut dalam artikel berikut:
Kesalahan lain adalah menggunakan analisis regresi dengan mengabaikan koefisien determinasi R-Kuadrat. Contoh menggunakan Regresi Berganda (Multiple Regression) sampai 10 variabel bebas, TETAPI R-Kuadrat sangat rendah! Besaran R-Kuadrat (Koefisien Determinasi) menunjukkan berapa persen total variasi (yang 100%) itu diterangkan oleh model statistika yang digunakan (dalam hal ini model regresi berganda–multiple regression).
Jika R-kuadrat misalnya HANYA 0,40; berarti model yang dibangun itu HANYA mampu menerangkan 40% keragaman dari obyek studi dalam populasi (total variasi = 100%); jadi 60% lainnya TIDAK BISA diterangkan oleh model statistika.
Apakah model statistika dengan kemampuan menerangkan total variasi HANYA 40% dapat diandalkan dan dipercayai? Seharusnya model statistika yang handal HARUS memiliki koefisien determinasi R-Kuadrat yang TINGGGI, katakanlah di atas 80%; sehingga model itu mampu menerangkan sampai minimum 80-an persen total variasi (yang 100%) itu.
Model dengan koefisien determinasi yang rendah, menunjukkan orang yang mendesain atau merumuskan model itu TIDAK BERKOMPETEN dalam bidang atau obyek yang sedang dipelajari dalam populasi.
Berbagai kesalahan umum lainnya dapat dibaca dalam Artikel berikut yang berjudul: Twenty Statistical Errors Even YOU Can Find in Biomedical Research Articles, agar kita tidak terus-menerus melakukan kesalahan-kesalahan prinsip yang berakibat kesimpulan atau hasil analisis STATISTIKA menjadi TIDAK VALID!
https://www.h2mw.eu/redactionmedicale/2010/10/CMJ%2020%20stat%20errors_T%20Lang_2004.pdf
Penjelasan berikut akan membahas Bagaimana dan Mengapa Penting Mengaitkan Pembelajaran Statistika di Perguruan Tinggi Indonesia dengan Kebutuhan Manajemen Bisnis Kelas Dunia? seperti ditunjukkan dalam Bagan 1 Terlampir.
Apa Itu Statistical Engineering Methods?
Adalah mustahil bagi kita untuk belajar dan memahami Statistical Engineering Methods tanpa memahami terlebih dahulu konsep dari systems thinking serta mengubah paradigma dan perilaku berpikir sistem (Systems Thinker) untuk memahami permasalahan yang ada dalam sistem.
Menurut Roger Hoerl (2019:1-19) Statistical Engineering adalah studi tentang integrasi sistematik antara konsep statistika, metode, dan alat-alat statistika, yang berkaitan secara langsung dengan disiplin ilmu-ilmu lain yang relevan, untuk memecahkan masalah-masalah penting dalam sistem kompleks secara berkelanjutan.
Statistical Engineering terdiri dari lima prinsip utama (Roger Hoerl, 2019: 11) berikut:
- Memahami masalah
- Mengembangkan strategi solusi masalah
- Mempertimbangkan asal usul data (data pedigree)
- Mengintegrasikan teori tentang permasalahan yang dihadapi
- Menggunakan pendekatan sekuensial (Merencanakan-Mengumpulkan Data-Menganalisis)
Selanjutnya ketika Statistical Engineering Methods itu diterapkan, maka langkah-langkah solusi masalah harus mengikuti enam langkah (Roger Hoerl, 2019:14) berikut:
- Mengidentifikasi masalah (Merumuskan masalah secara benar di dalam sistem).
- Menetapkan struktur masalah sistem (Memperjelas “kekacauan/mess”, Mendefinisikan masalah, dan Menetapkan sistem pengukuran).
- Memahami konteks (Sejarah, Politik, Kepribadian, dll).
- Mempertimbangkan strategi (Bagaimana menyelesaikan masalah, Menggunakan pendekatan sekuensial: merencanakan-mengumpulkan data-menganalisis berdasarkan teori ilmu pengetahuan, Menggunakan proses inti).
- Mengembangkan dan mengeksekusi taktik (Mengidentifikasi alternatif-alternatif, Memilih dan menerapkan metode-metode yang tepat).
- Mengidentifikasi dan menyebarluaskan keputusan akhir (Memverifikasi SUCCESS, Mempertahankan keberlanjutan/sustainability).
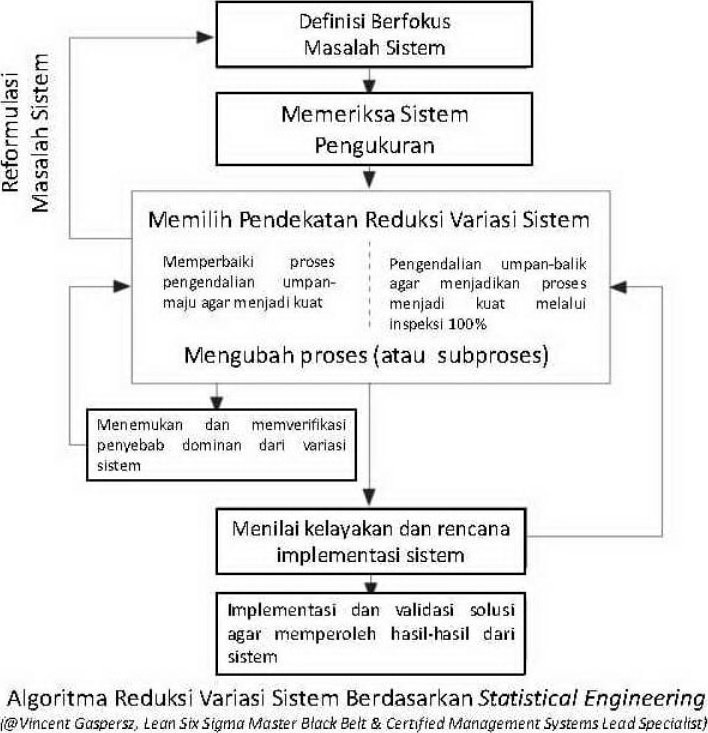
Berdasarkan pengalaman selama kurang lebih 30 tahun VG bekerja sebagai seorang Systems Designer and Implementor dalam industri, dunia usaha dan dunia kerja (IDUKA) yang berkualifikasi internasional sebagai Certified Management Systems Lead Specialist (CMSLS), maka ia menggunakan desain dan implementasi Statistical Engineering Methods yang telah didesain dan diterapkan secara luas untuk meningkatkan kinerja organisasi sebagai Systems of Systems (SoS), ditunjukkan dalam Bagan 2 terlampir.
Catatan VG: hal yang terasa aneh bagi VG, Statistical Engineering Methods yang sangat dibutuhkan oleh IDUKA ini TIDAK dipelajari oleh perguruan tinggi di Indonesia, sehingga lulusan perguruan tinggi di Indonesia TIDAK memiliki keterampilan Problem Solving & Decision Making yang berkaitan dengan masalah-masalah kompleks dalam sistem yang juga semakin kompleks karena keterkaitan dan kesalingtergantungan antara berbagai sistem-sistem yang membentuk organisasi sebagai Systems of Systems (SoS).
Statistical Thinking untuk Manajemen Sistem Kelas Dunia
Statistical Thinking (Pemikiran Statistika) adalah pendekatan yang telah diterima masyarakat profesional global, yang melibatkan penerapan metode ilmiah untuk memecahkan masalah- masalah kompleks dalam organisasi sebagai Systems of Systemsn (SoS) di dunia praktis (PRAKtek TIdak Sulit). Pendekatan ini dimulai dari mengumpulkan fakta melalui sistem pengukuran yang ada agar menjadi data, kemudian data diproses menggunakan statistical methods and tools untuk memperoleh informasi tentang faktor-faktor dominan penyebab variasi kinerja sistem organisasi itu. Selanjutnya menggunakan ilmu pengetahuan dan teknologi modern sesuai dengan masalah kinerja yang dihadapi, maka kita berusaha untuk melakukan reduiksi terus-menerus variasi kinerja dalam sistem organisasi itu berdasarkan solusi masalah dan pengambilan keputusan berbasis systems thinking and systems dynamics approach. Sasaran utama dari Statistical Thinking adalah mengoptimasikan kinerja dari sistem organisasi yang merupakan Systems of Systems (SoS) itu.
Statistical Thinking menurut Divisi Statistika American Society for Quality (ASQ, organisasi profesi kelas dunia dalam bidang Quality), adalah pemikiran filosofi ilmu statistika (philosophy of statistics) yang berkaiatan dengan tiga prinsip utama berikut: (1) Semua pekerjaan terjadi dalam proses-proses yang saling berhubungan di dalam sistem, (2) Variasi selalu ada di semua proses di dalam sistem, dan (3) Kunci SUCCESS adalah memahami proses dan mengurangi variasi di semua proses agar mencapai nilai TARGET yang diinginkan di dalam sistem. Sasaran utama dari filosofi berpikir statistika (statistical thinking) ini adalah kepuasan total kepada karyawan, pelanggan, pemegang saham, dan masyarakat. Berdasarkan hal ini, maka seseorang yang belajar ilmu statistika (statistics) tanpa mencapai sasaran atau tujuan utama ini disebutkan sebagai tidak memiliki pemikiran statistika (statistical thinking), karena hanya belajar pada level hirarki terendah dalam ilmu statistika, yaitu: Statistical Methods and Tools saja. Jelas pembelajaran hanya pada hirarki rendah dari ilmu statistika ini, maka akan menyulitkan seseorang yang hanya memahami Statistical Methods and Tools itu memasuki dan menempati posisi yang strategik dalam manajemen sistem bisnis kelas dunia. Penjelasan lebih mendalam tentang Statistical Thinking ini dapat dibaca dalam artikel berikut:
Lyne Hare, Roger Hoerl and Ronald Snee (1997) menyatakan bahwa seseorang yang memiliki pemikiran statistika akan melakukan beberapa hal berikut ketika berada dalam posisi manajemen bisnis kelas dunia. Mulai dari manajemen puncak (top management), manajemen menengah (middle management), dan manajemen bawah (lower management). Pembahasan berikut berkaitan dengan aplikasi statistical thinking pada masing-masing posisi manajemen bisnis kelas dunia.
Aplikasi Statistical Thinking pada Manajemen Puncak (Strategic Level & Top Management)
- Selalu menggunakan pendekatan sistem baik yang berkaitan dengan Systems Thinking maupun Systems Dynamics.
- Mentransformasikan proses-proses inti dalam sistem manajemen bisnis ke dalam diagram-diagram alir (flowcharts).
- Mendefinisikan dan menyebarluaskan analisis-analisis strategik menggunakan Strategic Thinking.
- Menetapkan sistem pengukuran kinerja yang bersifat kuantitatif maupun kualitatif kemudian berfokus pada pengelolaan indikator-indikator kinerja utama (Key Performance Indicators).
- Melakukan studi-studi benchmarking, termasuk umpan balik (feedback) dari karyawan (pelanggan internal), pelanggan eksternal, pemegang saham, dan masyarakat agar dipergunakan sebagai umpan-maju (feed forward) dalam perbaikan terus-menerus kinerja manajemen bisnis kelas dunia.
- Melakukan berbagai eksperimentasi untuk mengoptimumkan kinerja sistem bisnis kelas dunia.
Aplikasi Statistical Thinking pada Manajemen Menengah (Tactical Level & Middle Management)
- Manajer-manajer selalu menggunakan teknik-teknik pertemuan manajemen (management meetings) untuk memb ahas tentang perbaikan/peningkatan kinerja manajemen sistem bisnis kelas dunia itu.
- Menerapkan standardisasi program-program peningkatan kinerja berbasis sistem-sistem manajemen yang ada.
- Mengevaluasi dan meninjau ulang hasil-hasil dan proses-proses dari program-program perbaikan/peningkatan kinerja yang telah ditetapkan.
- Menetapkan tujuan dan sasaran (objectives and goals) perbaikan/peningkatan kinerja berbasiskan variasi proses dalam sistem manajemen bisnis kelas dunia itu.
- Menetapkan dan memperlakukan sistem pengukuran (Measurement Systems) sebagai suatu proses agar selalu konsisten menerapkan prinsip-prinsip Systems Thinking and Systems Dynamics.
- Berbagai pemasok dan input dalam sistem dan proses rantai nilai SIPOC (suppliers-Inputs-Processes-Outputs-Customers) dipergunakan atau ditetapkan sampai pada level optimum.
- Mempublikasikan kinerja sistem manajemen ke seluruh organisasi sebagai Systems of Systems (SoS) menggunakan berbagai jenis media komunikasi.
Aplikasi Statistical Thinking pada Manajemen Bawah (Operational Level & Lower Management)
- Mentransformasikan proses-proses kerja (working processes) ke dalam diagram-diagram alir (flowcharts), kemudian menerapkan dan mendokumentasikan secara tepat.
- Mengidentifikasi dan memonitor indikator-indikator kinerja kunci (Key Performance Indicators) secara harian/mingguan/bulanan/kuartal/ semester/tahunan.
- Menggunakan pengetahuan tentang variasi kinerja dalam sistem dan proses untuk melakukan perbaikan/peningkatan kinerja sistem dan proses.
- Mengubah paradigma agar semua aktivitas-aktivitas perbaikan/peningkatan kinerja sistem selalu berfokus pada proses menggunakan pendekatan Systems Thinking and Systems Dynamics, tanpa menyalahkan orang lain maupun lingkungan dari sistem manajemen organisasi kelas dunia itu.
Kesimpulan
Berdasarkan uraian dalam artikel ini, maka disimpulkan beberapa hal penting berikut.
- Pembelajaran statistika pada perguruan tinggi di Indonesia masih bersifat pembelajaran berpikir tingkat rendah (LOTS = Lower Order Thinking Skills) pada Statistical Methods and Tools dengan pemahaman yang terbatas, tanpa memahami Statistical Engineering Methods and Statistical Thinking, sehingga menyulitkan lulusan perguruan tinggi Indonesia memasuki pasar tenaga kerja nasional, regional, maupun global. Sebagai konsekuensi hanya mereka yang memiliki pemahaman yang baik tentang Statistical Engineering Methods and Statistical Thinking yang akan menempati posisi pada manajemen bisnis kelas dunia baik pada level strategik (manajemen puncak), level taktical (manajemen menengah), maupun level operasional (manajemen bawah), karena sistem bisnis kelas dunia telah menerapkan Systems Management yang berbasis pada Systems Thinking and Systems Dynamics.
- Agar memahami Statistical Engineering Methods and Statistical Thinking membutuhkan pemahaman penuh tentang sistem dan proses yang berlandaskan pada Systems Thinking and Systems Dynamics, selalu berfokus pada .ilmu pengetahuan statistika yang merupakan Ilmu Pengetahuan tentang Variasi (Variation Knowledge), bukan sekedar memahami rumus-rumus statistika sehingga mengkerdilkan ilmu statistika (statistics) seolah-olah hanya kumpulan tentang rumus-rumus matematika dan statistika saja.
- Agar mampu berkompetisi dan terlibat dalam berbagai posisi manajemen sistem bisnis kelas dunia, maka setiap orang harus berpikir untuk menyelesaikan masalah-masalah kompleks dalam sistem melalui reduksi variasi sistem dan proses secara terus- menerus, agar output dan outcome dari sistem apa saja itu mampu memberikan kepuasan total kepada karyawan (pelanggan internal), pelanggan eksternal, pemegang saham, maupun masyarakat.
- Pemahaman tentang Statistical Engineering Methods and Statistical Thinking akan menciptakan karakter seorang professional untuk selalu melakukan perbaikan/peningkatan kinerja terus-menerus, baik secara gradual atau incremental (Kaizen), maupun secara Radikal/Breakthrough/Innovation (Kaikaku/Six Sigma/ Disruptions Innovation).
- Memahami peranan data (atau big data) hanya sebagai bentuk pengukuran terhadap fakta saja adalah tidak cukup. Pemahaman terhadap data (atau big data) itu tidak sebatas berhenti pada analisis-analisis menggunakan Statistical Methods and Tools saja. Statistical Engineering Methods and Statistical Thinking itu adalah pembelajaran sampai pada tingkat sintesis, berupa: (a) mengkuantifikasikan variasi dan menurunkan variasi sistem secara terus-menerus, (b) mengukur dampak positif dari reduksi variasi sistem itu terhadap kepuasan total karyawan (pelanggan internal), pelanggan eksternal, pemegang saham, dan masyarakat, dan (c) melakukan tindakan koreksi dan pencegahan termasuk analisis-analisis risiko yang melekat dalam sistem bisnis kelas dunia itu, agar mampu mencapai tingkat optimum dari kinerja sistem manajemen bisnis dan industri kelas dunia.
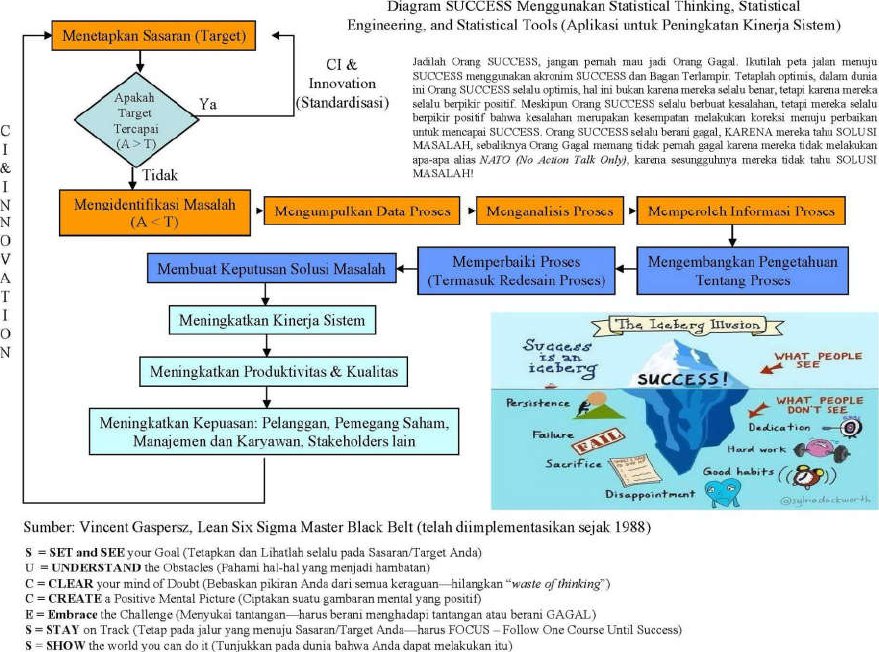
Integrasi aplikasi Statistical Thinking, Statistical Engineering Methods, and Statistical Methods and Tools yang dijelaskan dalam artikel ini dapat diringkaskan ke dalam satu bagan yang ditunjukkan dalam Bagan 3 terlampir.
Referensi
- Jim Duggan. Statistical Thinking for System Dynamics. Department of Information Technology, National University of Ireland, Galway. (pp. 1-16).
- Lyne Hare, Roger Hoerl, and Ronald Snee. 1997. How to Apply Statistical Thinking Effectively? FTC Short Course. 1997. (pp. 1-71).
- Roger Hoerl, and Roland Snee, 2002. Statistical Thinking: Improving Business Performance. Thompson Learning, Duxbury.
- Roger Hoerl. 2019. What is Statistical Engineering? Chapter 1, Setion 1, Statistical Engineering Handbook (pp. 1-19).
Artikel Vincent Gaspersz:
- http://www.vincentgaspersz.com/2016/07/15/bagaimana-mengaplikasikan-statistical-tools- statistical-engineering-dan-statistical-thinking-penjelasan-berdasarkan-pengalaman-aktual/?
- http://www.vincentgaspersz.com/2020/02/28/lots-mots-and-hots/?
- http://www.vincentgaspersz.com/2017/06/20/statistical-thinking-untuk-peningkatan-kinerja- sistem-bisnis/?
Linking Learning Statistics in Higher Education with World-Class Business Management Needs
By: Vincent Gaspersz, Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt & Certified Management Systems Lead Specialist
- APICS (www.apics.org) Certified in Production and Inventory Management (CPIM), Certified in Production and Inventory Management Fellow (CPIM-F), Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP), Certified Supply Chain Professional Fellow (CSCP-F);
- International Quality Federation (www.iqf.org) Six Sigma Master Black Belt (SSMBB);
- ASQ (www.asq.org) Certified Six Sigma Black Belt (CSSBB), Certified Quality Engineer (CQE), Certified Quality Auditor (CQA), Certified Manager of Quality/Organizational Excellence (CMQ/OE), Certified Quality Improvement Associate (CQIA);
- International Association for Six Sigma Certification (IASSC) Certified Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (ICBB);
- Registration Accreditation Board (www.exemplarglobal.org) Certified Management System Lead Specialist (CMSLS).
- Insinyur Profesional Utama (IPU) – Badan Kejuruan Teknik Industri- Persatuan Insinyur Indonesia (BKTI – PII)
- Asean Engineer Register (AER No. 10084), Asean Federation of Engineering Organizations (AFEO)
- Senior Member of the American Society for Quality (Member #: 00749775), International Member of the American Production and Inventory Control Society/Association for Supply Chain Management (Member #: 1023620), and Senior Member of the Institute of Industrial and Systems Engineers (Member #: 880194630).
As mentioned by Vincent Gaspersz so far, the Learning System in Indonesia is a low-level thinking learning (LOTS = Lower Order Thinking Skills), so that it is useless and unable to acquire modern science and technology that applies globally. To discuss and demonstrate this statement, it will be shown how statistics learning which are actually useful for competing in the global labor market is useless, because even higher education graduates, including statistics education graduates, cannot contribute significantly to management. world class business.
Statistics learning will only be useful if we study and understand the minimum to the intermediate level, namely learning about Statistical Engineering Methods that are useful for improving system performance, or are superior if we understand Statistical Thinking in order to contribute significantly in Systems Engineering and Systems Management.
Basically, Statistics has three hierarchies, namely: (1) Statistical Methods and Tools which are in the lowest hierarchy, (2) Statistical Engineering Methods which are in the middle hierarchy, and (3) Statistical Thinking which is in the highest hierarchy.
All students in Indonesia must have studied this Statistical Methods and Tools, although with very poor understanding and often applied it incorrectly due to a lack of understanding of the assumptions and requirements of the Statistical Methods and Tools application.
Frequently Made Mistakes
Mistakes are too often made and repeated continuously from the past until now in using statistical tools without understanding Statistical Engineering & Statistical Thinking!
Examples of common mistakes that are too often made by students and / or lecturers including scientists in reporting research results:
- Ho: X
- H1: Not X
Based on the statistical test blah blah blah, with a confidence level of 99%, then Ho is ACCEPTED!
This is a totally wrong conclusion, because it means that we don’t understand the principles of Statistics! Do we know that Ho is a statistical hypothesis that is NOT be ACCEPTED? The conclusion should be: based on the 99% confidence level using the xyz statistical test, there is not enough information to REJECT Ho. This DOES NOT MEAN WE ACCEPT Ho!
Each statistical test relating to hypothesis testing, ONLY provides the following two statistical conclusions:
- Rejecting Ho (with a certain level of confidence).
- Not enough information to Reject Ho (with a certain level of confidence); NOT (DOES NOT MEAN) Accepting Ho.
Please read the further explanation in the following article:
Another mistake is to use regression analysis by ignoring the R-Square coefficient of determination. Example using Multiple Regression (Multiple Regression) up to 10 independent variables, BUT R-Square is very low! The R-Square (coefficient of determination) indicates what percentage of the total variation (which is 100%) is explained by the statistical model used (in this case the multiple regression model).
If R-square for example ONLY 0.40; it means that the model built is ONLY able to explain 40% of the variation of the study object in the population (total variation = 100%); so the other 60% CANNOT be explained by statistical models.
Is the statistical model with the ability to explain the total variation of ONLY 40% reliable? A reliable statistical model MUST have a HIGH coefficient of determination R-Square, say above 80%; so that the model is able to explain up to a minimum of 80 percent of the total variation (which is 100%).
A model with a low coefficient of determination (R-square) indicates that the person who designs or formulates the model is NOT COMPETENT in the field or object being studied in the population.
Various other common mistakes can be read in the following article entitled: Twenty Statistical Errors Even YOU Can Find in Biomedical Research Articles, so that we don’t keep making mistakes in principle that result in the conclusions or results of the STATISTICAL analysis being NOT VALID!
https://www.h2mw.eu/redactionmedicale/2010/10/CMJ%2020%20stat%20errors_T%20Lang_2004.pdf
The following explanation will discuss How and Why is it Important to Link Learning Statistics in Indonesian Universities with the Needs of World-Class Business Management? as shown in the Attached Figure 1.

What Are Statistical Engineering Methods?
It is impossible for us to learn and understand Statistical Engineering Methods without first understanding the concept of systems thinking and changing the paradigm and behavior of systems thinking (Systems Thinker) to understand the problems that exist in the system.
According to Roger Hoerl (2019: 1-19) Statistical Engineering is the study of the systematic integration of statistical concepts, methods and statistical tools, which are directly related to other relevant disciplines, to solve important problems in systems. complex on an ongoing basis.
Statistical Engineering consists of the following five main principles (Roger Hoerl, 2019: 11):
- Understand the problem
- Develop a problem solution strategy
- Consider the origin of the data (pedigree data)
- Integrating theories about the problems at hand
- Using a sequential approach (Planning-Collecting Data-Analyzing)
Furthermore, when Statistical Engineering Methods are implemented, the steps for solving the problem must follow the following six steps (Roger Hoerl, 2019: 14):
- Identify the problem (Formulate the problem correctly in the system).
- Define the structure of the problem in the system (Clarify the “mess”, Define the problem, and Define the measurement system).
- Understand the context (History, Politics, Personalities, etc.).
- Consider strategies (How to solve problems, Using a sequential approach: planning-collecting data-analyzing based on scientific theory, Using core processes).
- Developing and executing tactics (Identifying alternatives, selecting and implementing appropriate methods).
- Identify and disseminate the final decision (Verify SUCCESS, Maintain sustainability).
Based on Vincent Gaspersz’s working experience during 30 years as a Systems Designer and Implementor in businesses and industries. with the international qualifications as a Certified Management Systems Lead Specialist (CMSLS), he uses the design and implementation of Statistical Engineering Methods that has been designed and widely applied to improve organizational performance as Systems of Systems (SoS), shown in the attached Figure 2.

Figure 2. Statistical Engineering Methods Algoritm to Reduce Variation in a System
Note: something that feels strange to Vincent Gaspersz (VG), the Statistical Engineering Methods that are needed by all world class business and industries are NOT studied by universities in Indonesia, so that university graduates in Indonesia do NOT have Problem Solving & Decision Making skills related to complex problems in the system. which is also increasingly complex because of the linkages and interdependence of the various systems that make up the organization as Systems of Systems (SoS).
Statistical Thinking for World Class Management Systems
Statistical Thinking is an approach that has been accepted by the global professional community, which involves the application of scientific methods to solve complex problems in organizations as Systems of Systems (SoS) in the practical world. This approach starts from collecting facts through existing measurement systems to become data, then the data is processed using statistical methods and tools to obtain information about the dominant factors causing variations in the performance of the organization’s systems. Furthermore, using modern science and technology in accordance with the performance problems faced, then we try to continually reduce performance variations in organizational systems based on problem solutions and decision making, based on systems thinking and systems dynamics approach. The main objective of Statistical Thinking is to optimize the performance of the organizational system which is the Systems of Systems (SoS).
According to the Statistics Division of the American Society for Quality (ASQ, a world-class professional organization in the field of Quality), Statistical Thinking is the philosophical thought of statistics (philosophy of statistics) which relates to the following three main principles: (1) All work occurs in processes that are interconnected in the system, (2) Variation is always present in all processes in the system, and (3) The key to SUCCESS is to understand the process and reduce variation in all processes in order to achieve the desired TARGET value in the system. The main goal of the philosophy of statistical thinking (statistical thinking) is total satisfaction to employees, customers, shareholders, and society. Based on this, someone who studies statistics without achieving this main goal or main objective is said to have no statistical thinking, because he/she only studies at the lowest hierarchical level in statistics, namely: Statistical Methods and Tools only. Obviously, learning only at this low hierarchy of statistics will make it difficult for someone who only understands Statistical Methods and Tools to enter and occupy a strategic position in world- class business system management. A more in-depth explanation of Statistical Thinking can be read in the following article:
Lyne Hare, Roger Hoerl and Ronald Snee (1997) state that a person with statistical thinking will do the following things when he/she is in a world-class business management position.
The following discussion relates to the application of statistical thinking in each of the world-class business management positions, starting from the top management (strategic level and top management), middle management (tactical level and middle management), and lower management (operational level and lower management).
Aplikasi Statistical Thinking pada Manajemen Puncak (Strategic Level & Top Management)
- Always using a systems approach related to Systems Thinking and Systems Dynamics.
- Transforming core processes in the business management system into flowcharts.
- Defining and disseminating strategic analysis using Strategic Thinking.
- Establish a quantitative and qualitative performance measurement system and then focus on managing the key performance indicators.
- Conduct benchmarking studies, including feedback from employees (internal customers), external customers, shareholders, and the public so that the information can be used as feed- forward in the continuous improvement of world-class business management performance.
- Carrying out various experimentations to optimize the performance of world-class business systems.
Application of Statistical Thinking in Middle Management (Tactical Level and Middle Management)
- Managers always using the techniques of management meetings to discuss the improvement of the management performance of the world class business system.
- Implementing standardization of performance improvement programs based on existing management systems.
- Evaluate and review the results and processes of the defined performance improvement programs.
- Setting goals and objectives of performance improvement, based focus on various processes in the world-class business management system.
- Establish and treat measurement systems (Measurement Systems) as a process in order to consistently apply the principles of Systems Thinking and Systems Dynamics.
- Various suppliers and inputs in the SIPOC (suppliers-Inputs-Processes-Outputs-Customers) value chain system and process are used or set to the optimum level.
- Publish performance management systems throughout the organization as Systems of Systems (SoS) using different types of communication media.
Application of Statistical Thinking in Lower Management (Operational Level and Lower Management)
- Transforming working processes into flowcharts, then applying and documenting appropriately.
- Identify and monitor Key Performance Indicators on a daily / weekly / monthly / quarterly / semester / annual basis.
- Using knowledge about performance variations in systems and processes to make improvements or/ enhancements to system and process performance.
- Change the paradigm so that all system performance improvement and/or improvement activities always focusing on the process using the Systems Thinking and Systems Dynamics approach, without blaming other people or the environment of the world-class organization’s management system.
Conclusion
Based on the description in this article, the following important things are concluded.
- Statistics learning at universities in Indonesia is still low-level thinking learning (LOTS = Lower Order Thinking Skills) on Statistical Methods and Tools with a limited understanding, without understanding Statistical Engineering Methods and Statistical Thinking, making it difficult for Indonesian higher education graduates to enter the labor market in national level, regional level and global level. As a consequence, only those who have a good understanding of Statistical Engineering Methods and Statistical Thinking will occupy a position in world-class business management at the strategic level (top management), the tactical level (middle management), or the operational level (lower management), because world-class business systems have implemented Management Systems based on Systems Thinking and Systems Dynamics.
- Understanding Statistical Engineering Methods and Statistical Thinking requires a full understanding of systems and processes based on Systems Thinking and Systems Dynamics, always focusing on statistical knowledge which is Variation Knowledge, not just understanding formulas. of statistics so that it dwarfs statistics as if it were only a collection of mathematical and statistical formulas.
- In order to be able to compete and to be involved in various world-class business system management positions, everyone must think about solving complex problems in the system through continuous reduction of variations in systems and processes, so that the outputs and outcomes of any system are capable provide total satisfaction to employees (internal customers), external customers, shareholders, and the public.
- An understanding of Statistical Engineering Methods and Statistical Thinking will create the character of a professional to always making improvements in performance continuously, either incremental (Kaizen), or Radical / Breakthrough / Innovation (Kaikaku / Six Sigma / Disruptions Innovation ).
- Understanding the role of data (or big data) as merely a measurement of facts is not sufficient. Understanding of data (or big data) is not limited to analyzes using Statistical Methods and Tools. Statistical Engineering Methods and Statistical Thinking are learning to the level of synthesis, in the form of: (a) quantifying variations and decreasing system variations continuously, (b) measuring the positive impact of reducing system variations on total employee satisfaction (internal customers), external customers, shareholders, and the public, and (c) take corrective and preventive actions including risk analysis inherent in the world-class business system, in order to achieve the optimum level of performance in world-class business and industrial management systems.
The integration of the Statistical Thinking, Statistical Engineering Methods, and Statistical Methods and Tools applications described in this article can be summarized into one chart shown in the attached Figure 3.

The Integration of the Statistical Thinking, Statistical Engineering, and Statistical Methods and Tools Applications
References
- Jim Duggan. Statistical Thinking for System Dynamics. Department of Information Technology, National University of Ireland, Galway. (pp. 1-16).
- Lyne Hare, Roger Hoerl, and Ronald Snee. 1997. How to Apply Statistical Thinking Effectively? FTC Short Course. 1997. (pp. 1-71).
- Roger Hoerl, and Roland Snee, 2002. Statistical Thinking: Improving Business Performance. Thompson Learning, Duxbury.
- Roger Hoerl. 2019. What is Statistical Engineering? Chapter 1, Setion 1, Statistical Engineering Handbook (pp. 1-19).
Articles of Vincent Gaspersz:
- http://www.vincentgaspersz.com/2016/07/15/bagaimana-mengaplikasikan-statistical-tools- statistical-engineering-dan-statistical-thinking-penjelasan-berdasarkan-pengalaman-aktual/?
- http://www.vincentgaspersz.com/2020/02/28/lots-mots-and-hots/?
- http://www.vincentgaspersz.com/2017/06/20/statistical-thinking-untuk-peningkatan-kinerja- sistem-bisnis/?